The application fields of acousto-optic modulators (AOM Modulator)
Principle of Acousto-optic modulator:
An acousto-optic modulator (AOM Modulator) is typically composed of acousto-optic crystals, transducers, absorption devices and drivers. The modulated signal output from the driver acts on the transducer in the form of an electrical signal and is then converted into an ultrasonic wave that varies in the form of an electrical signal. When the ultrasonic wave passes through the acousto-optic medium, it causes local compression and elongation of the medium, generating elastic strain. This strain changes periodically with time and space, causing the medium to exhibit an alternating density phenomenon, similar to a phase grating. When light passes through this medium disturbed by ultrasonic waves, a diffraction phenomenon occurs. This phenomenon is called the acousto-optic effect. Under the effect of sound and light, the optical carrier is modulated and becomes a modulated wave that “carries” information.
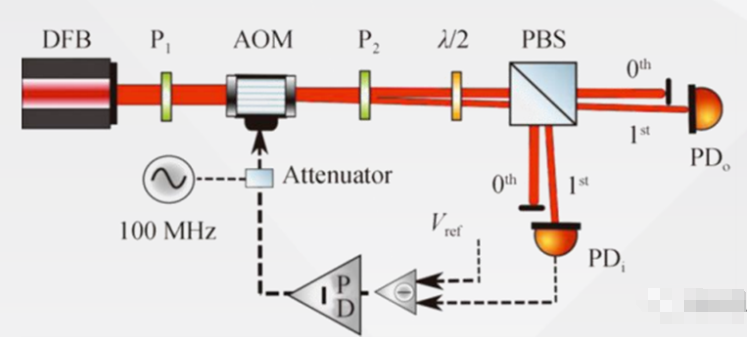
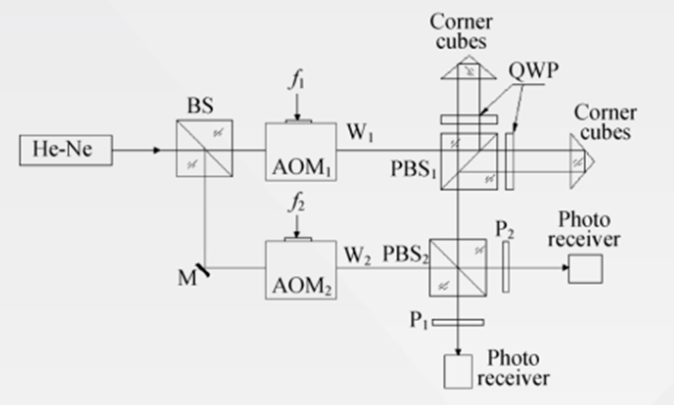
The main applications of acousto-optic modulators:
Sound and light Q Switch (AOQS)
The acoutooptic Q-switching switch (AOQS) operates within the laser cavity and is actively adjusted
The Q value in the cavity is used to generate pulsed lasers with short pulses and high peak power. AOQS is usually used to modulate the loss of the 0-order beam. When the radio frequency driver of AOQS is turned on, the 0-order light, due to diffraction, prevents the laser in the cavity from oscillating, increasing the cavity loss and blocking the laser output. When the radio frequency driver is briefly turned off, the accumulated optical power in the laser cavity is emitted in the form of pulses, thereby generating pulsed laser. This process can be repeated at a rate exceeding 100KHz. When AOQS operates in the Bragg state, there is only a single diffraction beam. in
There are multiple diffraction beams when working in the Raman – Niss state.
2. Acousto-optic Modulator/Switch (AOM Modulator)
Acousto-optic modulators (AOM) are generally used outside the laser cavity to change the intensity of the incident laser (amplitude modulation AM). This can be a simple ON/OFF modulation for rapid switching or variable level modulation to achieve intensity modulation. The modulation mode is determined by the type of RF driver and can be digital (on/off) or analog (sine, square wave, linear, random…). Generally speaking, the RF drive of AOM adopts a fixed frequency. The key parameter of AOM Modulator is the rise/fall time, which defines the achievable “speed” or amplitude modulation bandwidth of modulation. The rise/fall time is proportional to the beam diameter within the modulator. Therefore, in order to obtain a rapid ascent time, the diameter of the incident laser beam must be controlled. AOM can be used as a shutter (cycling on and off at a set frequency) and also as a variable attenuator (dynamically controlling the intensity of the transmitted light). Laser modulation is achieved by controlling the radio frequency to cause sound waves in the acousto-optic crystal.
3. Acousto-optic deflector (AODF)
The acoutooptic deflector (AODF) can achieve excited beam scanning by changing the radio frequency drive frequency. The scanning position can be random position, continuous line scanning and sequential point deflection. Based on the crystal, wavelength and beam size, a response time of 0.05 to 15 microseconds and precise position control of nRad can be achieved.
4. Acousto-optic frequency Shifter (AOFS)
After passing through all acousto-optic devices, the diffraction output beam of the laser beam will produce a frequency shift. The acousto-optic frequency shifter (AOFS) is a compact device specifically designed to achieve frequency shifting. Depending on the selected different incident angles, the AOFS will shift the frequency up or down by the frequency of the applied radio frequency signal, and two or more devices can be casccascted to achieve sum or difference frequency combinations. AOFS products adopt specially designed acoustic absorber angles, which can minimize sound reflection and enhance the efficiency of AOFS.
5. Acousto-optic Adjustable Filter (AOTF)
The acousto-optic tunable filter (AOTF) is a solid-state, electronically addressed and randomly accessed optical passband filter. It can be used to quickly and dynamically select specific wavelengths from broadband or multi-line sources. Diffraction occurs when specific matching conditions are met between acoustic beams. Therefore, it becomes possible to electronically control filter parameters (such as wavelength, modulation depth, and even bandwidth), thereby providing fast (usually microseconds), dynamic, and random access to optical filtering.
Post time: May-26-2025





