The key items of photodetector testing
The bandwidth and rise time (also known as response time) of photodetectors, as key items in the testing of detectors, have currently attracted the attention of many optoelectronic researchers. However, the author has found that many people have no understanding of these two parameters at all. Today, JIMu Optoresearch will specifically introduce the bandwidth and rise time of photodetectors to everyone.
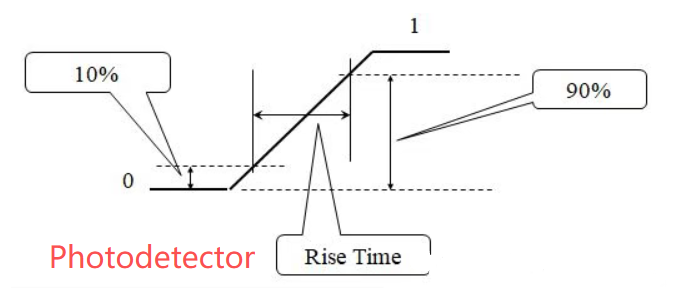
In the previous article on the selection of core parameters for photodiodes, we introduced that both the rise time (τr) and the fall time (τf) are key indicators for measuring the response speed of photodetectors. The 3dB bandwidth, as an indicator in the frequency domain, is closely related to the rise time in terms of response speed. The relationship between the bandwidth BW of a photodetector and its response time Tr can be roughly converted by the following formula: Tr=0.35/BW.
Rise time is a term in pulse technology, describing and meaning that the signal rises from one point (usually: Vout*10%) to another point (usually: Vout*90%). The amplitude of the rising edge of the Rise Time signal generally refers to the time taken to rise from 10% to 90%. Test principle: The signal is transmitted along a certain path, and another sampling head is used to obtain and measure the voltage pulse value at the remote end.
The rise time of the signal is crucial for understanding signal integrity issues. The vast majority of problems related to product application performance in the design of high-speed photodetector are associated with it. When selecting a photodetector, you must pay sufficient attention to it. It is important that we establish the concept that the rise time has a significant impact on circuit performance. As long as it is within a certain range, it must be taken seriously, even if it is a very vague range. There is no need to precisely define this range standard, nor is it of practical significance. Just remember that the current chip processing technology has made this time very short, reaching the ps level. It’s time for you to pay attention to its impact.
As the signal rise time decreases, problems such as reflection, crosstalk, orbit collapse, electromagnetic radiation, and ground bounce caused by the internal signal or output signal of the photodetector become more severe, and the noise problem becomes more difficult to solve. From the perspective of spectral analysis, the reduction of signal rise time is equivalent to an increase in signal bandwidth, that is, there are more high-frequency components in the signal. It is precisely these high-frequency components that make the design difficult. Interconnection lines must be treated as transmission lines, which has led to many problems that did not exist before.
Therefore, in the application process of photodetectors, you must have such a concept: when the output signal of the photodetector has a steep rising edge or even severe overshoot, and the signal is unstable, it is very likely that the photodetector you purchased does not meet the relevant design requirements for signal integrity and cannot meet your actual application requirements in terms of bandwidth and rise time parameters. The photoelectric detector products of JIMU Guangyan all sample the latest advanced photoelectric chips, high-speed operational amplifier chips, and precise filter circuits. According to the actual application signal characteristics of customers, they match the bandwidth and rise time. Every step takes into account the integrity of the signal. Avoid common problems such as high signal noise and poor stability caused by mismatch between bandwidth and rise time in the application of photodetectors for users.
Post time: Sep-15-2025





