What is a acousto-optic modulator AOM modulator
Acousto-optic modulation is an external modulation technique. Generally, the acousto-optic device that controls the intensity variation of the laser beam is called an acousto-optic modulator (AOM modulator). The modulated signal acts on the electroacoustic transducer in the form of an electrical signal (amplitude modulation), and is then converted into an ultrasonic field that changes in the form of an electrical signal. When light waves pass through the acousto-optic medium, due to the acousto-optic effect, the optical carrier is modulated and becomes an intensity modulated wave that “carries” information.
Working principle
Acousto-optic modulation is a physical process that uses the acousto-optic effect to load information onto an optical frequency carrier. The modulated signal acts on the electroacoustic transducer in the form of an electrical signal (amplitude modulation), and is then converted into an ultrasonic field that changes in the form of an electrical signal. When light waves pass through the acousto-optic medium, due to the acousto-optic effect, the optical carrier is modulated and becomes an intensity modulated wave that “carries” information.
An acousto-optic modulator (AOM modulator) is typically composed of acousto-optic crystals, transducers, absorption devices and drivers. The modulated signal output from the driver acts on the transducer in the form of an electrical signal and is then converted into an ultrasonic wave that varies in the form of an electrical signal. When the ultrasonic wave passes through the acousto-optic medium, it causes local compression and elongation of the medium, generating elastic strain. This strain changes periodically with time and space, causing the medium to exhibit an alternating density phenomenon, similar to a phase grating. When light passes through this medium disturbed by ultrasonic waves, a diffraction phenomenon occurs. This phenomenon is called the acousto-optic effect. Under the effect of sound and light, the optical carrier is modulated and becomes a modulated wave that “carries” information.
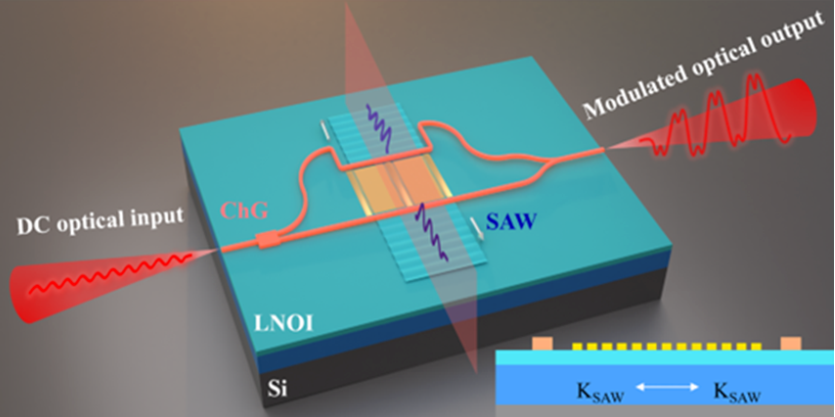
Briefly describe the main parameters
Diffraction efficiency and modulation loss
2. Bragg Angle: When incident light is input into an acousto-optic device at a Bragg Angle, the best diffraction efficiency can be achieved. Angular errors will reduce efficiency.
3. Divergence Angle adaptation
4. Modulation speed: The optical switching time is defined by the transmission time of the sound wave through the beam waist in the A0 crystal.
5. Optimal RF Power (Saturation Power)
Post time: Jun-04-2025





