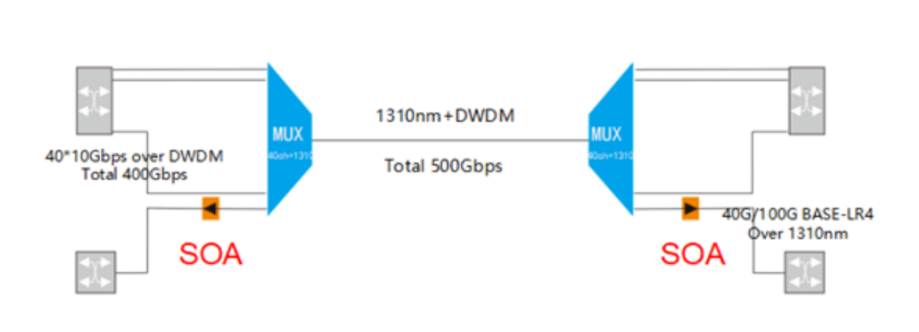
Enhanced semiconductor optical amplifier
The enhanced semiconductor optical amplifier is an upgraded version of the semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA optical amplifier). It is an amplifier that uses semiconductors to provide the gain medium. Its structure is similar to that of the Fabry-Pero laser diode, but usually the end face is coated with an anti-reflection film. The latest design includes anti-reflection films as well as inclined waveguides and window regions, which can reduce the end face reflectivity to below 0.001%. High-performance enhanced optical amplifiers are particularly useful when amplifying (optical) signals, as there is a serious threat of signal loss during long-distance transmission. Since the optical signal is directly amplified, the traditional way of converting it into an electrical signal before becomes redundant. Therefore, the use of SOA significantly improves the transmission efficiency. This technology is usually used for power division and loss compensation in WDM networks.
Application scenarios
In optical fiber communication systems, semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOA) can be used in multiple application areas to enhance the performance and transmission distance of the communication system. The following are some common applications of using SOA amplifier in optical fiber communication systems:
Preamplifier: SOA optical amplifier can be used as a preamplifier at the optical receiving end in long-distance communication systems with optical fibers exceeding 100 kilometers, enhancing or amplifying the strength of the signal output in long-distance optical fiber communication systems, thereby compensating for the insufficient transmission distance caused by weak output of small signals. Furthermore, SOA can also be used to implement the optical network signal regeneration technology in optical fiber communication systems.
All-optical signal regeneration: In optical networks, as the transmission distance increases, optical signals will deteriorate due to attenuation, dispersion, noise, time jitter and crosstalk, etc. Therefore, in long-distance transmission, it is necessary to compensate for the deteriorated optical signals to ensure the accuracy of the transmitted information. All-optical signal regeneration refers to re-amplification, re-shaping and re-timing. Further amplification can be accomplished by optical amplifiers such as semiconductor optical amplifiers, EDFA and Raman amplifiers (RFA).
In optical fiber sensing systems, semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOA amplifier) can be used to amplify optical signals, thereby enhancing the sensitivity and accuracy of the sensors. The following are some common applications of using SOA in optical fiber sensing systems:
Optical fiber strain measurement: Fix the optical fiber on the object whose strain needs to be measured. When the object is subjected to strain, the change in strain will cause a slight change in the length of the optical fiber, thereby altering the wavelength or timing of the optical signal to the PD sensor. SOA amplifier can achieve higher sensing performance by amplifying and processing the optical signal.
Optical fiber pressure measurement: By combining optical fibers with pressure-sensitive materials, when an object is subjected to pressure, it will cause changes in the optical loss within the optical fiber. SOA can be used to amplify this weak optical signal to achieve highly sensitive pressure measurement.
The semiconductor optical amplifier SOA is a key device in the fields of optical fiber communication and optical fiber sensing. By amplifying and processing optical signals, it enhances system performance and sensing sensitivity. These applications are crucial for achieving high-speed, stable and reliable optical fiber communication as well as precise and efficient optical fiber sensing.
Post time: Apr-29-2025





