The cutting-edge applications in optics led by optical modulators
The principle of optical modulation is not complicated. It mainly achieves the modulation of the amplitude, phase, polarization, refractive index, absorption rate and other characteristics of light through external stimuli, to precisely control the optical signal, such as enabling photons to carry and transmit information. The basic components of a common electro-optic modulator include three parts: electro-optic crystals, electrodes, and optical elements. During the process of light modulation, the material in the optical modulator changes its refractive index, absorption rate and other properties under the influence of external stimuli (such as electric fields, sound fields, thermal changes or mechanical forces), thereby affecting the behavior of photons as they pass through the material, such as controlling the propagation characteristics of light (amplitude, phase, polarization, etc.). The electro-optical crystal is the core of the optical modulator, responsible for responding to changes in the electric field and altering its refractive index. Electrodes are used to apply electric fields, while optical components such as polarizers and waveplates are used to guide and analyze photons passing through the crystal.
Frontier Applications in Optics
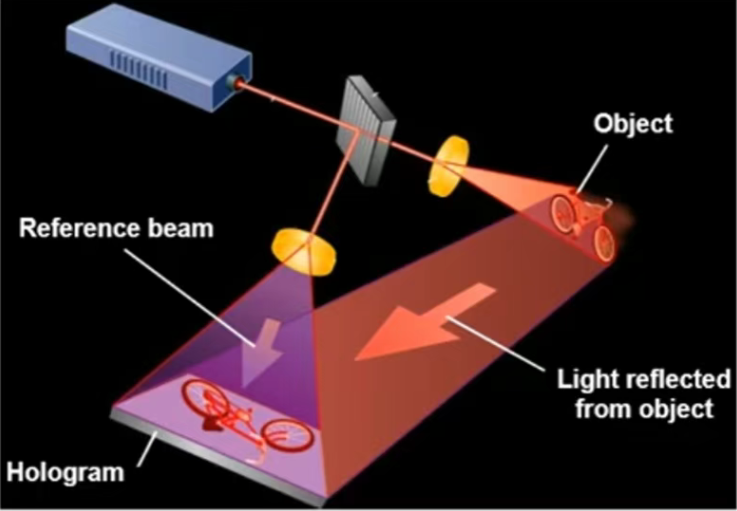
1.Holographic projection and display technology
In holographic projection, the use of spatial optical modulators to finely modulate the incident light waves can enable the light waves to interfere and diffract in a specific way, forming a complex light field distribution. For instance, SLM based on liquid crystal or DMD can dynamically adjust the optical response of each pixel, change the image content or perspective in real time, allowing viewers to observe the three-dimensional effect of the image from different angles.
2.Optical data storage field
Optical data storage technology utilizes the high-frequency and high-energy characteristics of light to encode and decode information through precise light modulation. This technology relies on the precise control of light waves, including the adjustment of amplitude, phase and polarization state, to store data on media such as optical discs or holographic storage materials. Optical modulators, especially spatial optical modulators, play a crucial role in allowing for highly precise optical control over the storage and reading processes.
On the optical stage, photons are like exquisite dancers, gracefully dancing to the “melody” of materials such as crystals, liquid crystals and optical fibers. They can elegantly change direction, speed, and even instantly put on different “colored costumes”, transforming their movements and rhythms, and presenting one spectacular performance after another. This precise control of photons is precisely the magical key to the cutting-edge of future optical technology, making the optical world full of infinite possibilities.
Post time: Jul-09-2025





