The Mach-Zehnder Modulator (MZ Modulator) is an important device for modulating optical signals based on the interference principle. Its working principle is as follows: At the Y-shaped branch at the input end, the input light is divided into two light waves and enters two parallel optical channels for transmission respectively. The optical channel is made of electro-optic materials. By taking advantage of its photoelectric effect, when the externally applied electrical signal changes, the refractive index of its own material can be altered, resulting in different optical path differences between the two beams of light reaching the Y-shaped branch at the output end. When the optical signals in the two optical channels reach the Y-shaped branch at the output end, convergence will occur. Due to the different phase delays of the two optical signals, interference occurs between them, converting the phase difference information carried by the two optical signals into the intensity information of the output signal. Therefore, the function of modulating electrical signals onto optical carriers can be achieved by controlling various parameters of the loading voltage of the March-Zehnder modulator.
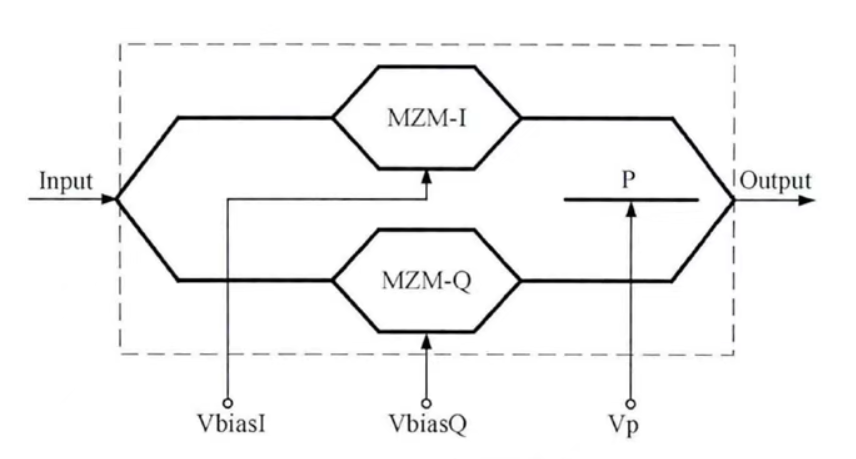
The basic parameters of MZ Modulator
The basic parameters of the MZ Modulator directly affect the performance of the modulator in various application scenarios. Among them, the important optical parameters and electrical parameters are as follows.
Optical parameters:
(1) Optical bandwidth (3db bandwidth) : The frequency range when the frequency response amplitude decreases by 3db from the maximum value, with the unit being Ghz. Optical bandwidth reflects the frequency range of the signal when the modulator is operating normally and is a parameter for measuring the information carrying capacity of the optical carrier in the electro-optic modulator.
(2) Extinction ratio: The ratio of the maximum optical power output by the electro-optic modulator to the minimum optical power, with the unit of dB. The extinction ratio is a parameter for evaluating the electro-optic switch capability of a modulator.
(3) Return loss: The ratio of the reflected light power at the input end of the modulator to the input light power, with the unit of dB. Return loss is a parameter that reflects the incident power reflected back to the signal source.
(4) Insertion loss: The ratio of the output optical power to the input optical power of a modulator when it reaches its maximum output power, with the unit being dB. Insertion loss is an indicator that measures the optical power loss caused by the insertion of an optical path.
(5) Maximum input optical power: During normal use, the MZM Modulator input optical power should be less than this value to prevent device damage, with the unit being mW.
(6) Modulation depth: It refers to the ratio of the modulation signal amplitude to the carrier amplitude, usually expressed as a percentage.
Electrical parameters:
Half-wave voltage: It refers to the voltage difference required for the driving voltage to switch the modulator from the off state to the on state. The output optical power of MZM Modulator varies continuously with the change of bias voltage. When the modulator output generates a 180-degree phase difference, the difference in bias voltage corresponding to the adjacent minimum point and the maximum point is the half-wave voltage, with the unit of V. This parameter is determined by factors such as material, structure and process, and is an inherent parameter of MZM Modulator.
(2) Maximum DC bias voltage: During normal use, the input bias voltage of MZM should be less than this value to prevent device damage. The unit is V. The DC bias voltage is used to control the bias state of the modulator to meet different modulation requirements.
(3) Maximum RF signal value: During normal use, the input RF electrical signal of the MZM should be less than this value to prevent device damage. The unit is V. A radio frequency signal is an electrical signal that is to be modulated onto an optical carrier.
Post time: Jun-16-2025





