Optical Wireless Communication (OWC) is a form of optical communication in which signals are transmitted using unguided visible, infrared (IR), or ultraviolet (UV) light.
OWC systems operating at visible wavelengths (390 — 750 nm) are often referred to as visible light communication (VLC). VLC systems take advantage of light-emitting diodes (leds) and can pulse at very high speeds without noticeable effects on lighting output and the human eye. VLC can be used in a wide range of applications including wireless LAN, wireless personal LAN and vehicle networking. On the other hand, ground-based point-to-point OWC systems, also known as free space optics (FSO) systems, operate at near-infrared frequencies (750 — 1600 nm). These systems typically use laser emitters and offer cost-effective protocol transparent links with high data rates (i.e. 10 Gbit/s per wavelength) and provide a potential solution to backhaul bottlenecks. Interest in ultraviolet communication (UVC) is also growing due to recent advances in solid-state light sources/detectors operating in the sun-blind UV spectrum (200 — 280 nm). In this so-called deep ultraviolet band, solar radiation is negligible at ground level, making possible the design of a photon-counting detector with a wide-field receiver that increases the received energy without adding additional background noise.
For decades, interest in optical wireless communications has been limited primarily to clandestine military applications and space applications including intersatellite and deep space links. To date, OWC’s mass market penetration has been limited, but IrDA is a highly successful wireless short-range transmission solution.
From optical interconnection in integrated circuits to outdoor interbuilding links to satellite communications, variants of optical wireless communication can potentially be used in a wide variety of communication applications.
Optical wireless communication can be divided into five categories according to transmission range:
1. Super short distances
Interchip communication in stacked and tightly packed multi-chip packages.
2. Short distances
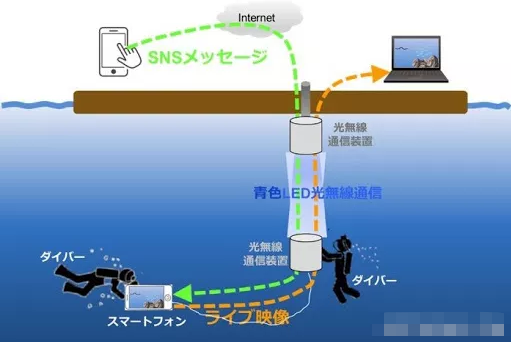
In the standard IEEE 802.15.7, underwater communication under wireless Body Local Area Network (WBAN) and wireless Personal Local Area Network (WPAN) applications.
3. Medium range
Indoor IR and visible light communication (VLC) for wireless local area networks (WLans) as well as vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication.
Step 4: Remote
Interbuilding connectivity, also known as free space optical communication (FSO).
5. Extra distance
Laser communication in space, especially for links between satellites and the establishment of satellite constellations.
Post time: Jun-01-2023